Climatic and Thermal Testing
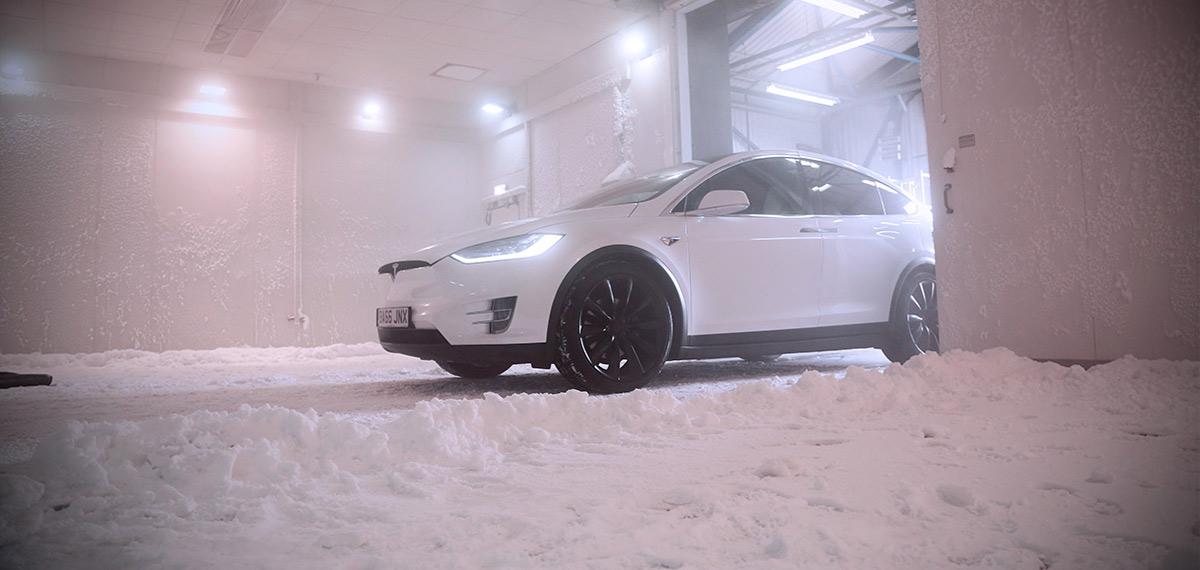

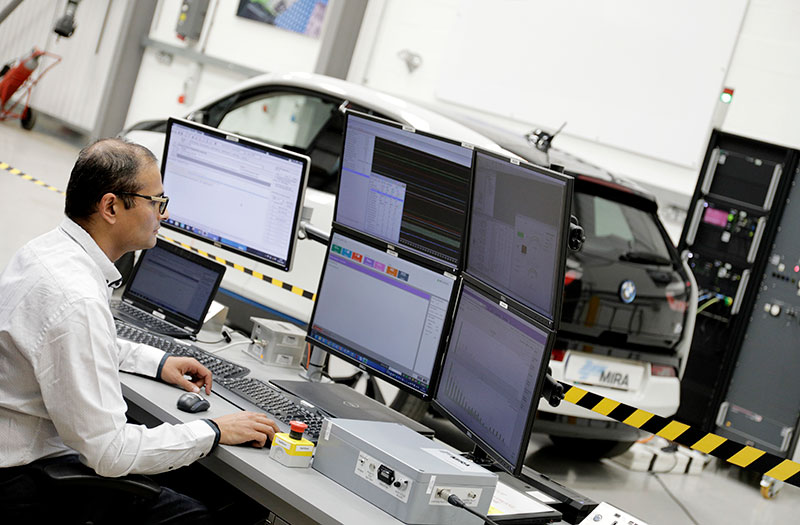
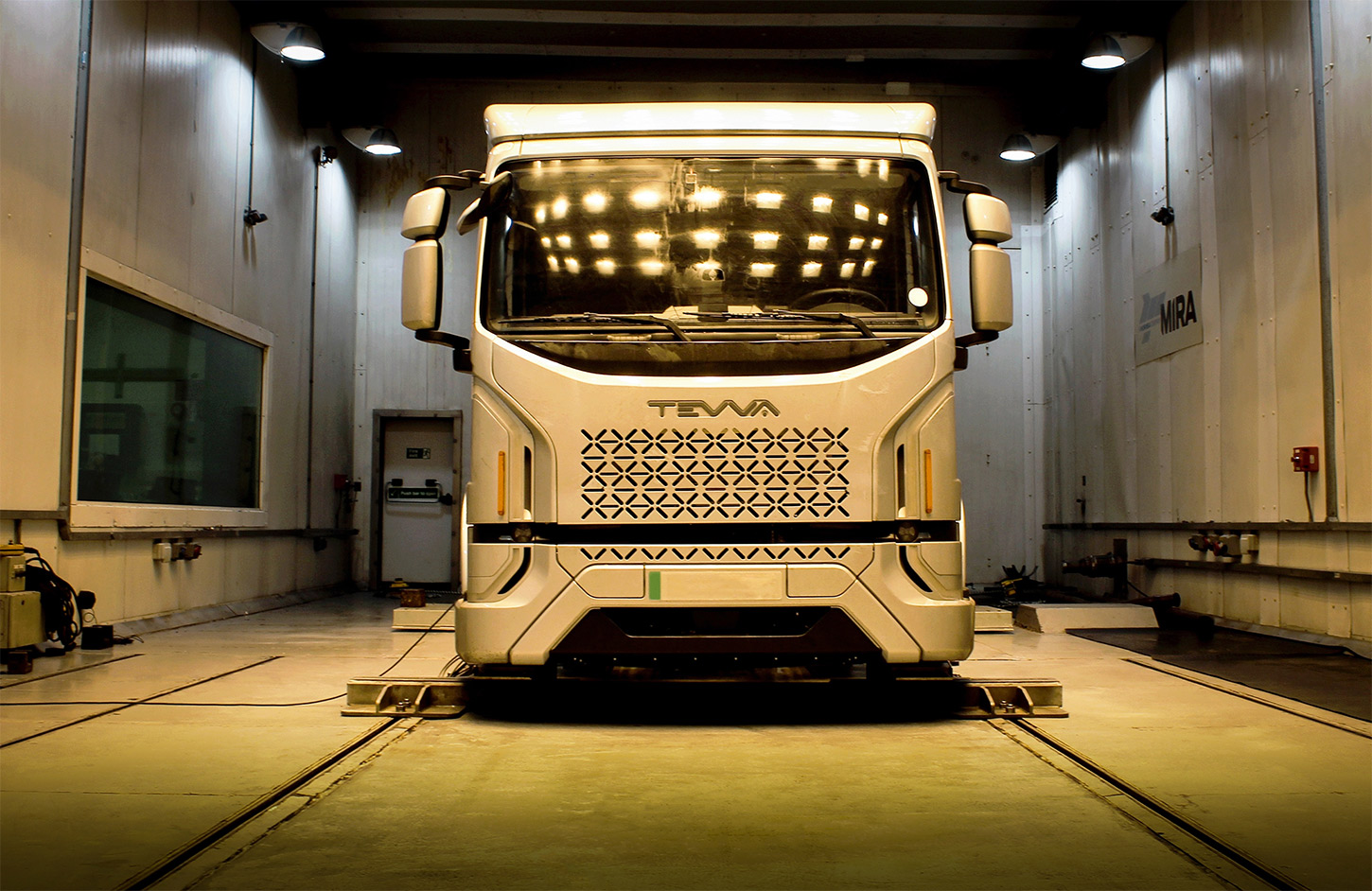
When engineering and testing vehicles, various climatic tests are conducted to ensure that vehicles can operate safely and reliably under different environmental conditions.
These tests help assess the performance and durability of a vehicle in extreme climates and are essential for product development and validation.
The main types of climatic tests carried out for vehicles include:
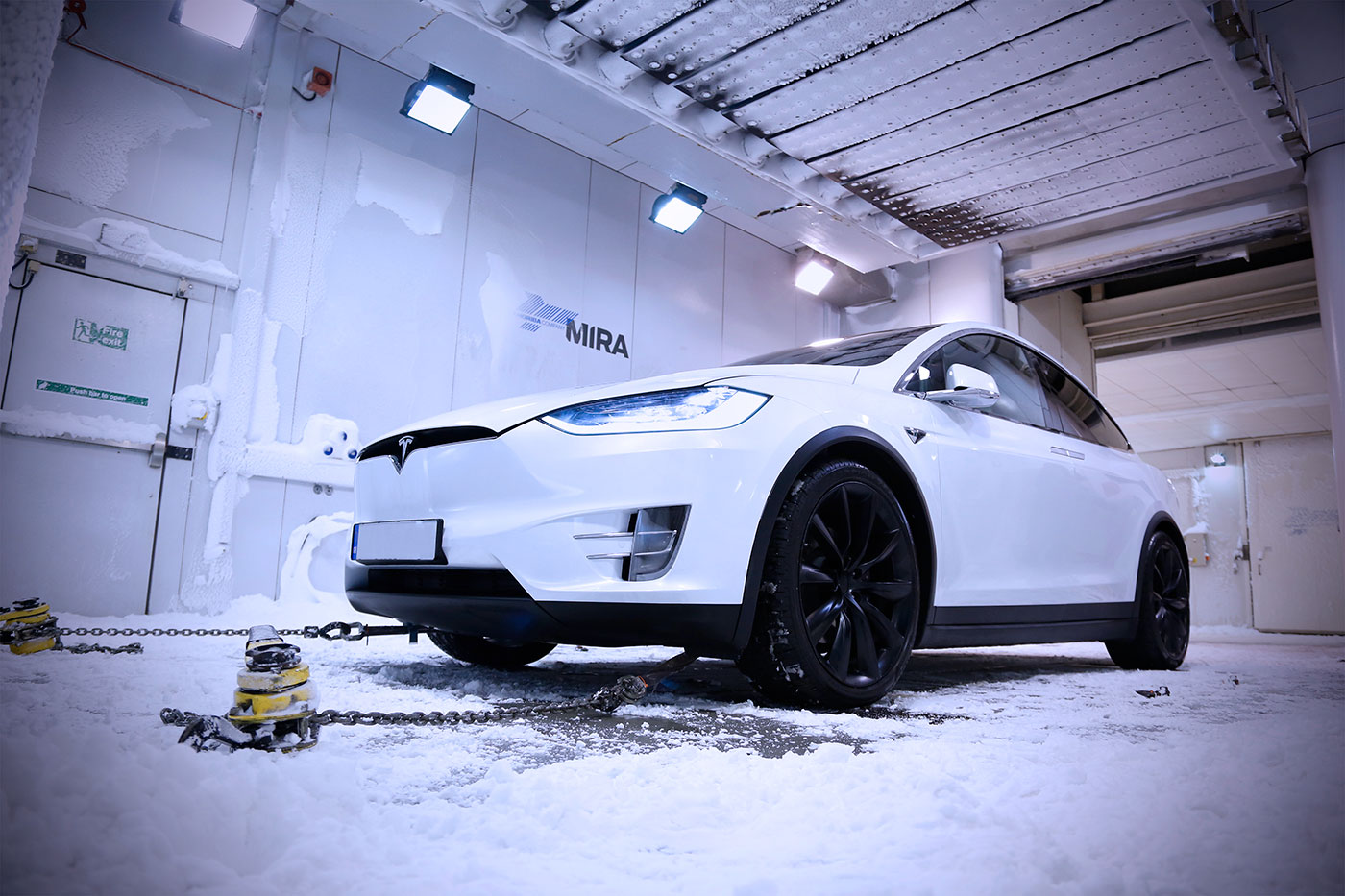
Cold Weather Testing
- Cold Start Testing: This involves starting and operating the vehicle in extremely cold temperatures to evaluate engine performance, battery capacity, lubrication systems, and the effectiveness of heating systems.
- Cold Soak Testing: The vehicle is exposed to very low temperatures for an extended period to assess the performance of materials, fluids, and systems at low temperatures, including the impact on plastics, rubber components, and fuel systems.
- Icing and Snow Testing: Evaluates the vehicle’s ability to handle snow and ice on the road, including traction control, braking performance, and the effectiveness of heating and defrosting systems.
Hot Weather Testing
- Hot Weather Performance Testing: Measures how well the vehicle’s engine and cooling systems perform under high-temperature conditions, checking for overheating and coolant system efficiency.
- Air Conditioning Testing: Ensures that the vehicle’s air conditioning system can provide adequate cooling and cabin comfort in hot weather.
- Sun Load Testing: Evaluates the impact of intense sunlight and heat on interior materials, electronics, and the effectiveness of sunshades and tinted windows.
Humidity Testing
- High Humidity Testing: Examines how the vehicle’s components and systems withstand high levels of humidity, which can lead to corrosion, electrical issues, and mold growth.
- Humidity and Temperature Cycling: Subjects the vehicle to rapid and repeated changes in temperature and humidity to assess its durability and the potential for moisture-related problems.
Altitude Testing
- High Altitude Testing: Measures the vehicle’s performance at high altitudes, where reduced air pressure and lower oxygen levels can affect engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions.
Salt Spray Testing
- Salt Fog Testing: Involves exposing the vehicle to a saltwater mist to evaluate corrosion resistance, particularly for components susceptible to rust.
Dust and Sand Testing
- Dust and Sand Ingress Testing: Evaluates how well the vehicle’s seals and filters prevent the entry of dust and sand, which can damage mechanical components and electronics.
Rain and Water Testing
- Water Ingress Testing: Assesses the vehicle’s ability to prevent water from entering the cabin or critical components during heavy rain or flooding.
Thermal Shock Testing
- Thermal Cycling Testing: Subjects the vehicle to rapid temperature changes to evaluate its ability to withstand thermal stress, which can lead to material fatigue and component failures.
Vibration and Shock Testing
- Vibration Testing: Simulates the effects of road vibrations on the vehicle to assess the durability and performance of various components.
- Shock Testing: Tests the vehicle’s ability to withstand sudden shocks or impacts, such as potholes or rough terrain.
Speak to an Expert
If you would like to discuss your testing requirements with one of our experts, please send us a message and we will contact you as soon as possible.